Understanding Credit Score: The Impact and How to Improve It. Understanding credit scores is essential for managing your financial health effectively. Your bank score affects everything from your ability to obtain loans to the interest rates you receive. In this article, we will dive into the fundamentals of credit scores, their importance, how they’re calculated, and practical ways to improve your score over time.
What is a Credit Score?
A bank score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness, usually ranging from 300 to 850. This score helps lenders decide if you’re a reliable borrower. Higher scores indicate responsible credit behavior, while lower scores may signal a riskier borrower.
Why is Your Credit Score Important?
- Loan Approval and Interest Rates: A good bank score increases your chances of loan approvals with favorable interest rates.
- Impact on Employment: Many employers review bank scores for insight into a candidate’s reliability.
- Insurance Premiums: Insurance companies may use your bank score to determine premiums, as they see it as an indicator of responsibility.
- Housing Opportunities: Landlords often review bank scores when renting out properties.
- Security Deposits: Utility and cell phone companies may waive security deposits for customers with high bank scores.
How is a Credit Score Calculated?
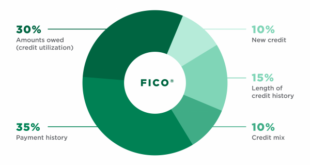
Bank scores are calculated based on five primary factors:
- Payment History (35%): This is the largest factor in determining your score. Late payments can significantly lower your credit score.
- Credit Utilization (30%): This represents how much of your available credit you’re using. High utilization can negatively impact your score.
- Length of Credit History (15%): The longer your credit history, the better.
- Credit Mix (10%): A variety of credit types, such as credit cards and loans, can positively affect your score.
- New Credit (10%): Frequently applying for new credit can lower your score, as it indicates a potential financial risk.
Types of Credit Scores:
- FICO Score: Widely used in the U.S., ranging from 300 to 850.
- VantageScore: Another common score range, also from 300 to 850.
- Other Scoring Models: Different lenders may use alternative models tailored to specific lending criteria.
How to Check Your Credit Score
Most people can check their bank score for free through various services, and each bureau allows one free report per year. Monitoring your score is essential for understanding your financial health and for catching any potential errors.
Steps to Improve Your Credit Score
- Pay Bills on Time: Your payment history has the most significant impact on your score.
- Reduce Credit Card Balances: Try to keep your credit utilization ratio below 30%.
- Avoid Opening New Accounts Frequently: Each new account generates a hard inquiry that may reduce your score slightly.
- Keep Old Accounts Open: Older accounts contribute positively to your credit history length.
- Diversify Credit Types: Having a mix of credit accounts can improve your score.
Mistakes to Avoid When Managing Your Credit Score
- Making Late Payments: This directly impacts your score.
- Applying for Multiple Loans at Once: Can suggest financial instability to lenders.
- Ignoring Your Credit Report: Errors can occur, and you should dispute them if they do.
- Closing Old Accounts: Reduces your credit history length and affects the score.
- Using Maximum Credit Limits: High balances signal financial distress.
10 Tips for Improving Your Credit Score
- Regularly check your credit report for errors.
- Pay your bills on time.
- Aim to use less than 30% of your credit limit.
- Set up automatic payments to avoid missed payments.
- Diversify your credit mix.
- Keep old accounts open.
- Avoid closing unused credit cards.
- Limit new credit applications.
- Dispute inaccuracies in your report.
- Seek professional advice if needed.
10 FAQs about Credit Scores
- What is considered a good bank score?
- A score above 700 is generally good, while over 800 is excellent.
- How often should I check my credit report?
- At least once a year from each bureau.
- Can I get a loan with a low bank score?
- Yes, but it may come with higher interest rates.
- How long do late payments affect my credit score?
- Late payments stay on your report for seven years.
- Will checking my own credit score lower it?
- No, checking your score through a soft inquiry does not impact it.
- Do utility payments affect my credit score?
- Yes, if reported to credit bureaus.
- Is it good to have multiple credit cards?
- It can help if managed well; high balances on multiple cards can hurt your score.
- How does divorce affect my credit score?
- Divorce itself does not, but joint accounts may influence it.
- Can I improve my score by paying off loans early?
- Paying loans on time benefits your score more than paying off early.
- Do student loans impact credit scores?
- Yes, they are considered part of your credit history.
Conclusion
Understanding your bank score and its components is crucial for achieving financial success. A good score not only opens doors for better financial products but also helps you save money through lower interest rates. By following the tips provided and avoiding common mistakes, you can build and maintain a strong credit profile over time. Monitoring and improving your bank score is an ongoing process, but the rewards are well worth the effort for a financially secure future.
 credit.suarajatim.com
credit.suarajatim.com