Financial Credit Review: Guide to Evaluating Your Credit. Financial credit review plays a pivotal role in shaping an individual’s financial health. Whether you are looking to apply for a loan, buy a house, or simply track your financial standing, understanding your credit is essential. This article delves into the importance of financial credit review, how to conduct one, and what it can reveal about your financial habits. With insights into credit reports, scores, and improvement strategies, this guide will help you take control of your financial future.
What is Financial Credit Review?
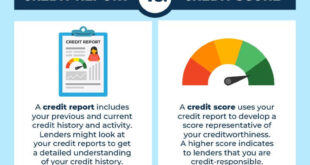
A financial credit review is the process of assessing an individual’s credit history and creditworthiness. It involves analyzing the information in your credit report, such as your payment history, outstanding debts, credit utilization, and recent credit inquiries. This review helps lenders and financial institutions gauge the risk of lending to you. It is crucial for consumers to regularly monitor their credit reports to ensure accuracy and identify any areas that need improvement.
Why Is Financial Credit Review Important?
A financial credit review is important for several reasons:
- Loan and Credit Approval: Lenders use your credit report to determine whether you qualify for a loan or credit card. A higher credit score generally means better loan terms and lower interest rates.
- Detecting Errors: Mistakes in your credit report can negatively affect your credit score. Regularly reviewing your credit report can help spot these errors and address them quickly.
- Improving Credit Score: Regular credit reviews allow you to monitor your credit score and make the necessary changes to improve it over time, which can benefit you when applying for future credit.
- Financial Awareness: Understanding where you stand financially empowers you to make informed decisions, helping you plan for large purchases or investments.
The Components of a Credit Report
A credit report contains several key components that a financial credit review examines:
- Personal Information: Includes your name, address, social security number, and employment details.
- Credit Accounts: Information about your open and closed accounts, including the type of account (e.g., credit cards, mortgages), credit limits, and outstanding balances.
- Payment History: Shows your record of paying bills on time, or any late payments, bankruptcies, or foreclosures.
- Credit Inquiries: Tracks who has checked your credit in the past 24 months. This includes hard inquiries (when a lender checks your credit for a loan) and soft inquiries (like checking your own credit score).
- Public Records: Includes any public financial issues such as bankruptcies, foreclosures, or judgments.
How to Conduct a Financial Credit Review
Conducting a thorough financial credit review involves several steps. Here’s a simplified process to help you get started:
- Obtain Your Credit Reports: Request a copy of your credit report from one of the three major credit bureaus—Equifax, Experian, or TransUnion. In many countries, consumers are entitled to a free report once a year.
- Check for Accuracy: Go through the details of your credit report carefully. Look for discrepancies, such as incorrect account balances, unfamiliar accounts, or late payments that you don’t recognize.
- Analyze Your Credit Score: Your credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness. A score below 580 is typically considered poor, while scores above 700 are considered good. It’s important to understand how your score is calculated.
- Identify Areas for Improvement: If your score is lower than desired, identify the key factors affecting it. These could include high credit utilization, missed payments, or too many recent credit inquiries.
- Dispute Errors: If you find inaccuracies in your credit report, dispute them with the relevant credit bureau. They are legally required to investigate and correct errors within 30 days.
- Take Steps to Improve Your Credit: Based on your review, take action to improve your credit score. Pay off outstanding debts, reduce your credit card balances, and ensure timely bill payments.
How Financial Institutions Use Credit Reviews
Lenders rely heavily on credit reviews to evaluate an applicant’s ability to repay a loan. Here’s how they use the data:
- Loan Approvals: Financial institutions use credit reports to determine whether you qualify for credit. They assess the likelihood that you will repay the loan based on your past credit behavior.
- Interest Rates: A higher credit score often results in better loan terms, such as lower interest rates. The lower your credit risk, the more favorable your loan conditions.
- Credit Limit Decisions: Your credit limit is determined based on your credit report and score. A better credit report means a higher credit limit, which provides more flexibility in your financial decisions.
Common Mistakes That Can Lower Your Credit Score
Here are some common mistakes that can negatively affect your credit score:
- Missing Payments: Late or missed payments can significantly hurt your credit score. Aim to make all payments on time.
- High Credit Utilization: Using a large portion of your available credit can lower your score. Try to keep your credit utilization below 30%.
- Opening Too Many New Accounts: Frequent applications for new credit can lead to multiple inquiries, which can lower your credit score.
- Closing Old Accounts: Closing older credit accounts may shorten your credit history and negatively impact your credit score.
- Not Reviewing Your Credit Report: Failing to monitor your credit report means missing potential errors or fraudulent activity.
Strategies to Improve Your Credit Score
Improving your credit score is a gradual process that requires careful planning. Here are some effective strategies:
- Pay Bills On Time: Timely payments are one of the most significant factors affecting your credit score.
- Reduce Outstanding Debts: Paying down your debts, especially credit card balances, can significantly improve your credit score.
- Diversify Your Credit: Having a mix of credit types, such as credit cards, installment loans, and retail accounts, can improve your score.
- Avoid Opening New Credit Accounts: Refrain from opening too many new credit accounts to avoid unnecessary hard inquiries.
- Dispute Errors: Correcting inaccuracies in your credit report can help improve your score in the short term.
10 Tips for a Successful Financial Credit Review
- Regularly check your credit report for errors.
- Set reminders to pay bills on time.
- Keep your credit card balances low.
- Dispute any inaccuracies with the credit bureaus immediately.
- Avoid applying for too many credit cards or loans in a short time.
- Work on paying off existing debt.
- Maintain a mix of credit types to show diverse credit management.
- Use credit monitoring services for ongoing updates.
- Set a budget to prevent overspending.
- Monitor your credit utilization ratio and keep it under 30%.
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- How often should I review my credit report?
- It’s recommended to review your credit report at least once a year, but if you’re planning a major purchase or loan, check it more frequently.
- How long does a credit review take?
- A financial credit review can take anywhere from 30 minutes to an hour, depending on how detailed you want to be.
- Can checking my own credit score hurt it?
- No, checking your own score is a soft inquiry and does not affect your credit score.
- What is considered a good credit score?
- A score of 700 or higher is generally considered good, with 750 or above considered excellent.
- What should I do if I find an error in my credit report?
- Dispute the error with the relevant credit bureau, providing proof of the mistake.
- How can I improve my credit score quickly?
- Paying down high credit card balances and making on-time payments can help improve your score in the short term.
- Does a financial credit review affect my score?
- A personal credit review (soft inquiry) does not affect your score, but a lender’s inquiry (hard inquiry) can have a small impact.
- Can I get a loan with bad credit?
- It is possible, but you may face higher interest rates or need a co-signer.
- How long does negative information stay on my credit report?
- Negative items, such as missed payments or bankruptcies, typically stay on your report for seven to ten years.
- Is it important to have a diverse credit history?
- Yes, having a mix of different types of credit can improve your credit score and show lenders that you can handle various financial responsibilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a financial credit review is an essential tool for understanding your financial health and improving your credit score. By regularly reviewing your credit report, identifying areas for improvement, and taking proactive steps, you can enhance your creditworthiness and access better financial opportunities. Remember, maintaining a healthy credit score is a long-term commitment that requires diligence, but the rewards are worth the effort.
A solid credit score can open doors to lower interest rates, higher loan limits, and greater financial freedom. So, make it a habit to regularly check your credit report, dispute errors, and implement strategies to improve your credit score over time. With consistent effort and knowledge, you can ensure your financial future remains secure and bright.
 credit.suarajatim.com
credit.suarajatim.com