Track Credit History: Understanding and Managing Your Credit. Understanding and managing your credit history is vital for financial well-being. Whether you’re looking to apply for a loan, get a mortgage, or simply improve your financial health, keeping track of your credit history is crucial. This article explores how to track credit history, the benefits of monitoring it regularly, and tips to improve it.
What Is Credit History?
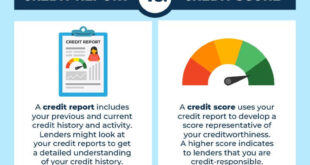
- Definition of Credit History: A record of your borrowing and repayment activities.
- Components of Credit History: Payment history, outstanding debts, credit inquiries, and credit accounts.
Why Tracking Credit History Is Important
- Financial Decision Making: Understanding credit history helps in making better financial choices.
- Credit Score Monitoring: Regularly tracking credit history helps maintain or improve your credit score.
- Fraud Prevention: Detecting unauthorized activities early on.
How to Track Your Credit History
- Free Annual Credit Reports: Learn how to get free credit reports from all three major credit bureaus annually (Equifax, Experian, TransUnion).
- Credit Monitoring Services: Explore options for both free and paid services to track credit history in real-time.
- Credit Score Tools: Use online tools and apps to monitor your credit score regularly.
- Using Your Bank or Credit Card Provider: Many financial institutions provide credit score tracking as a feature of their service.
How Credit History Impacts Your Life
- Loan Approval: Lenders use your credit history to determine whether you qualify for loans or credit cards.
- Interest Rates: A better credit history can lead to lower interest rates.
- Employment Opportunities: Employers may check credit history as part of the hiring process for certain roles.
How to Improve Your Credit History
- Timely Bill Payments: Consistently paying your bills on time helps build a positive credit history.
- Reducing Outstanding Debts: Pay down your credit card balances to improve your debt-to-income ratio.
- Avoiding Excessive Credit Applications: Limit the number of credit applications to avoid negative marks on your history.
- Building Credit from Scratch: For those with no credit history, applying for a secured credit card can be a good starting point.
Common Credit History Myths
- Checking Your Own Credit History Lowers Your Score: Myth debunked—checking your own credit does not affect your score.
- Closing Old Accounts Improves Credit: Why closing old credit accounts can harm your credit score.
- Bad Credit History Lasts Forever: Learn how negative marks fall off your credit history after a certain period.
Tools to Track Credit History
- Credit Report Websites: Discover the best websites for getting detailed reports.
- Apps and Software: Recommendations for apps that help with ongoing credit monitoring.
- Credit Score Alerts: Use services that send you alerts whenever there’s a change to your credit score or report.
How Often Should You Track Your Credit History?
- Annual Credit Reports: Check your credit reports at least once a year.
- Monthly or Quarterly Tracking: For those with active credit, monthly tracking is recommended.
- After Major Financial Events: Whenever you apply for a loan or face a financial hardship, it’s essential to review your credit history.
Potential Consequences of Ignoring Your Credit History
- Missed Financial Opportunities: Not tracking credit could result in higher loan interest rates or denial.
- Increased Fraud Risk: Ignoring credit history increases the risk of undetected fraud or identity theft.
Conclusion
Tracking your credit history is a fundamental aspect of managing your financial life. It empowers you to make informed decisions, catch errors early, and prevent fraud. By regularly reviewing your credit history and understanding how it affects your financial opportunities, you can improve your credit score, lower your interest rates, and secure better financial outcomes.
10 Tips for Tracking Your Credit History
- Get Your Free Annual Report: Claim your free credit report from the three bureaus every year.
- Use Free Credit Score Services: Take advantage of tools like Credit Karma or Credit Sesame.
- Set Up Alerts: Enable notifications for any significant changes to your credit report.
- Look for Errors: Always verify the accuracy of the information on your credit report.
- Monitor Your Credit Score Regularly: Stay informed by checking your score monthly or quarterly.
- Secure Your Information: Use strong passwords and two-factor authentication for online accounts.
- Reduce Your Credit Utilization: Keep your balances low to improve your credit score.
- Dispute Incorrect Information: If you find inaccuracies, dispute them immediately.
- Keep Track of Your Debts: Pay off outstanding balances to avoid negatively affecting your credit history.
- Understand Your Credit Report: Learn how to interpret your credit report to spot potential issues.
10 FAQs about Tracking Credit History
- How often should I check my credit history?
It’s advisable to check at least once a year for free reports, and monthly for ongoing monitoring. - Does checking my own credit history hurt my score?
No, checking your own credit report is a “soft inquiry” and does not affect your score. - What is a credit report?
A credit report is a detailed record of your borrowing and repayment history, created by credit bureaus. - Can I track my credit score for free?
Yes, there are several services available that offer free credit score tracking, such as Credit Karma. - What’s the difference between credit history and credit score?
Your credit history is a record of your borrowing behavior, while your credit score is a numerical value representing that history. - Why is it important to monitor my credit history?
Monitoring helps you identify errors, spot identity theft early, and understand how financial decisions affect your score. - How long do negative marks stay on my credit report?
Most negative marks, like late payments, stay on your report for up to 7 years. - What happens if I don’t track my credit history?
Not monitoring your credit increases the risk of fraud and missed opportunities for financial improvement. - Can employers check my credit history?
Yes, some employers may review your credit history during the hiring process, especially for financial roles. - Can I remove negative marks from my credit report?
Negative marks can only be removed if they are inaccurate or after the allotted time has passed.
Conclusion
Tracking your credit history is essential for maintaining financial health. By staying on top of your credit reports, utilizing free tools, and keeping track of changes, you can safeguard your financial future. Not only does it help in avoiding fraud, but it also allows for better financial decisions and opportunities. Regular tracking ensures you understand your credit standing and can act quickly if problems arise.
 credit.suarajatim.com
credit.suarajatim.com