Credit Score Range: Improving and Maximizing Your Credit. A credit score is a numerical representation of a person’s creditworthiness, influencing financial decisions such as loan approvals, credit card limits, and mortgage rates. Understanding the credit score range is essential for managing your financial health effectively. This article will cover the different credit score ranges, factors affecting scores, ways to improve credit, and common FAQs.
Understanding Credit Score Ranges
Credit scores typically range from 300 to 850, with different categories that indicate financial reliability. Below are the commonly accepted credit score ranges:
- 300 – 579: Poor
- Individuals with scores in this range may struggle to obtain loans or credit approvals.
- Higher interest rates and stricter lending terms apply.
- 580 – 669: Fair
- Some lenders approve loans for fair credit holders, but interest rates remain relatively high.
- It is advisable to improve credit before applying for large loans.
- 670 – 739: Good
- This range is considered favorable by lenders.
- Borrowers typically receive competitive interest rates and better credit options.
- 740 – 799: Very Good
- Indicates a strong credit profile with excellent financial behavior.
- Credit approvals are easier, and interest rates are lower.
- 800 – 850: Excellent
- The highest range with the best financial benefits.
- Borrowers in this category qualify for the lowest interest rates and premium credit offers.
Factors Affecting Your Credit Score
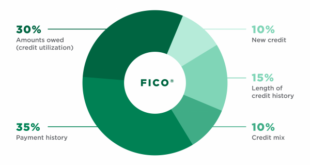
Your credit score is determined by multiple factors, with each having a specific weight:
- Payment History (35%)
- Late or missed payments negatively impact your score.
- Credit Utilization (30%)
- Using more than 30% of your available credit limit can lower your score.
- Credit History Length (15%)
- A longer credit history contributes positively to your score.
- New Credit Inquiries (10%)
- Multiple hard inquiries in a short time can decrease your score.
- Credit Mix (10%)
- A diverse credit portfolio (loans, credit cards, mortgages) can improve your score.
How to Improve Your Credit Score
- Pay Bills on Time – Ensure timely payments to avoid penalties.
- Reduce Credit Utilization – Keep credit card balances low, ideally below 30% of your limit.
- Avoid Opening Too Many Accounts – Excessive inquiries can lower your score.
- Maintain Old Accounts – A long credit history helps improve your score.
- Monitor Your Credit Report – Check for errors and dispute inaccuracies.
- Diversify Credit Types – A good mix of installment and revolving credit is beneficial.
- Use Secured Credit Cards – If you have bad credit, a secured card can help rebuild it.
- Negotiate Debt Settlements – Work with creditors to settle outstanding debts responsibly.
- Become an Authorized User – Being added to a responsible user’s credit card can boost your score.
- Avoid Closing Accounts – Keeping old accounts open helps maintain credit history length.
10 Essential Tips for Managing Credit Score
- Set up automatic payments to never miss a due date.
- Use credit responsibly by charging only what you can pay off monthly.
- Avoid carrying high credit card balances.
- Check your credit score regularly for unexpected changes.
- Limit applications for new credit cards and loans.
- Pay off high-interest debts first to reduce financial burden.
- Establish an emergency fund to avoid using credit for unexpected expenses.
- Keep credit inquiries to a minimum.
- Understand how different types of credit impact your score.
- Work with a credit counselor if struggling with debt management.
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the best credit score to have?
- A score of 800 or above is considered excellent.
- How long does it take to improve a credit score?
- It depends on individual circumstances but can take months to years.
- Will checking my credit score lower it?
- No, checking your own score is a soft inquiry and does not affect your score.
- How often should I check my credit score?
- At least once a year, or more frequently if monitoring credit changes.
- Can I get a loan with a low credit score?
- Yes, but interest rates will likely be high.
- What happens if I miss a credit card payment?
- Late payments can lower your score and result in fees.
- Does closing a credit card improve my score?
- No, it can actually lower your score by reducing your available credit.
- How does credit utilization affect my score?
- High utilization can lower your score, while keeping it low helps improve it.
- Do all lenders use the same credit scoring model?
- No, lenders may use different models such as FICO or VantageScore.
- Can bankruptcy ruin my credit score permanently?
- No, but it stays on your report for up to 10 years and significantly impacts your score.
Conclusion
Your credit score range plays a vital role in financial decisions, from securing loans to obtaining low-interest credit cards. By understanding where you stand in the credit score spectrum, you can take necessary steps to improve and maintain a healthy credit profile. Paying bills on time, keeping credit utilization low, and monitoring your credit report regularly can significantly boost your score.
Managing your credit responsibly ensures better financial opportunities, lower interest rates, and increased approval chances for loans and credit cards. Stay proactive in maintaining good credit habits, and over time, you will see the benefits reflected in your financial stability and creditworthiness.
 credit.suarajatim.com
credit.suarajatim.com