Credit Score Meaning: Importance and How to Improve It. A credit score is a numerical representation of an individual’s creditworthiness. It plays a crucial role in determining eligibility for loans, credit cards, and even rental agreements. Understanding credit scores can help you take control of your financial health and secure better financial opportunities.
What is a Credit Score?
A credit score is a three-digit number that represents your creditworthiness based on your financial history. Lenders, landlords, and even some employers use this score to evaluate the risk of lending to or engaging in financial transactions with an individual. The most commonly used credit scoring models are FICO Score and VantageScore.
How is a Credit Score Calculated?
Credit scores are determined using several factors, including:
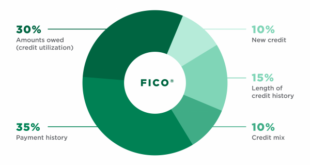
- Payment History (35%) – Whether you pay your bills on time.
- Credit Utilization (30%) – The ratio of your current credit balance to your credit limit.
- Length of Credit History (15%) – How long your credit accounts have been active.
- Credit Mix (10%) – The variety of credit accounts you have, such as loans, mortgages, and credit cards.
- New Credit Inquiries (10%) – The number of recent applications for new credit.
Why is a Credit Score Important?
A good credit score can open doors to better financial opportunities, such as:
- Lower Interest Rates – Higher credit scores often qualify for lower interest rates on loans and credit cards.
- Easier Loan Approvals – Lenders prefer applicants with high credit scores, making it easier to get approved.
- Better Credit Card Offers – High scores lead to premium credit cards with rewards and benefits.
- Higher Loan Limits – A strong credit history increases the amount of credit you can access.
- Favorable Rental Agreements – Many landlords check credit scores before approving tenants.
Credit Score Ranges
Credit scores typically fall into the following ranges:
- 300-579: Poor – High risk for lenders.
- 580-669: Fair – Subprime borrowers.
- 670-739: Good – Acceptable credit risk.
- 740-799: Very Good – Low risk for lenders.
- 800-850: Excellent – Ideal credit score for best rates and offers.
How to Check Your Credit Score
You can check your credit score through:
- Credit Bureaus – Major bureaus like Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion provide credit reports.
- Credit Card Providers – Many banks offer free credit score tracking.
- Online Credit Monitoring Services – Websites like Credit Karma provide free access to credit scores.
How to Improve Your Credit Score
- Pay Bills on Time – Late payments negatively impact your credit score.
- Reduce Credit Utilization – Keep credit card balances below 30% of the credit limit.
- Avoid Opening Too Many Accounts – Too many hard inquiries can lower your score.
- Diversify Credit Accounts – Having a mix of credit types can boost your score.
- Dispute Errors on Credit Report – Regularly review and correct inaccuracies.
- Keep Old Accounts Open – Longer credit history improves your score.
- Limit New Credit Applications – Too many credit inquiries can lower your score.
- Use Secured Credit Cards – These can help build credit if you have a low score.
- Negotiate with Creditors – Ask for better repayment terms or lower interest rates.
- Monitor Your Credit Score Regularly – Keeping track helps prevent fraud and errors.
10 Tips to Maintain a High Credit Score
- Always pay your bills before the due date.
- Keep your credit utilization low.
- Avoid maxing out your credit cards.
- Set up automatic payments to avoid late fees.
- Regularly check your credit report for errors.
- Use different types of credit responsibly.
- Avoid closing old credit accounts unnecessarily.
- Don’t apply for too many loans at once.
- Keep your debt-to-income ratio low.
- Stay informed about changes in credit scoring models.
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a good credit score?
A score of 700 or higher is generally considered good, with 800+ being excellent.
2. How often should I check my credit score?
You should check your credit score at least once a month to monitor for any inaccuracies.
3. Does checking my credit score lower it?
No, checking your own credit score is a soft inquiry and does not affect your score.
4. How long do late payments affect my credit score?
Late payments stay on your credit report for seven years, but their impact diminishes over time.
5. Can I improve my credit score quickly?
Yes, by paying off debts, reducing credit utilization, and correcting errors on your report.
6. Do student loans affect credit scores?
Yes, student loans impact your credit score just like any other type of debt.
7. Can closing a credit card hurt my score?
Yes, closing a card can decrease your available credit and shorten your credit history.
8. How long does it take to build credit?
It typically takes six months to a year to build a fair credit score from scratch.
9. Can bankruptcy ruin my credit score?
Yes, bankruptcy can severely lower your score and stays on your report for 7-10 years.
10. Does renting a house affect my credit score?
Some landlords report rental payments, which can help or hurt your credit score depending on payment history.
Conclusion
Your credit score is a powerful financial tool that affects your ability to secure loans, get better interest rates, and even rent a home. Maintaining a good credit score requires consistent effort, such as timely payments, keeping credit utilization low, and monitoring your credit report regularly.
By following the strategies outlined in this guide, you can improve your credit score and enjoy the financial benefits that come with it. Being proactive in managing your credit health ensures long-term financial stability and greater financial freedom.
 credit.suarajatim.com
credit.suarajatim.com