Background Credit Check: Understanding Its Importance and Process. In today’s world, background credit checks have become an integral part of various industries, particularly in financial services, employment, and housing. These checks assess an individual’s credit history, providing valuable insights into their financial behavior. Understanding the ins and outs of background credit checks is crucial for consumers, employers, and landlords alike. This article will explore the definition, significance, and process of background credit checks, as well as tips for managing credit history effectively.
What Is a Background Credit Check?
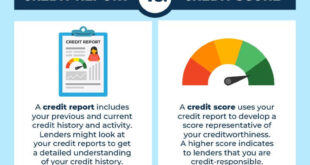
A background credit check is an evaluation of an individual’s credit history conducted by lenders, employers, landlords, or financial institutions. This process typically involves reviewing an individual’s credit report, which contains detailed information about their borrowing and repayment behavior, outstanding debts, payment history, and credit inquiries.
Credit checks can be categorized into two main types:
- Soft Inquiries: These checks do not affect a person’s credit score and can occur when an individual checks their credit or when a company checks an individual’s credit for promotional purposes.
- Hard Inquiries: These checks occur when a financial institution or lender reviews an individual’s credit report as part of their decision-making process for lending. Hard inquiries can temporarily lower a person’s credit score.
Why Are Background Credit Checks Important?
Background credit checks serve multiple purposes across various sectors:
- Lending Decisions: Lenders use credit checks to assess an applicant’s creditworthiness before approving loans. A strong credit history increases the likelihood of loan approval and better interest rates.
- Employment Screening: Employers often conduct credit checks to evaluate potential employees, especially for positions that involve financial responsibilities. A poor credit history may raise concerns about an individual’s reliability and trustworthiness.
- Rental Agreements: Landlords perform credit checks on prospective tenants to ensure they can meet rental obligations. A positive credit history indicates financial responsibility, while a negative history may lead to rental application denials.
- Insurance Premiums: Insurance companies may use credit checks to determine premiums for policies. A better credit score can lead to lower premiums.
The Process of Conducting a Background Credit Check
Conducting a background credit check typically involves several steps:
- Obtaining Consent: Before conducting a credit check, entities must obtain written consent from the individual being checked. This is a legal requirement to ensure privacy.
- Choosing a Credit Reporting Agency: Lenders, employers, and landlords usually work with one of the three major credit bureaus—Equifax, Experian, or TransUnion—to obtain the credit report.
- Reviewing the Credit Report: Once the report is obtained, the entity reviews the individual’s credit history, including outstanding debts, payment history, and any public records such as bankruptcies.
- Making Decisions: Based on the information found in the credit report, the entity will make informed decisions regarding lending, hiring, or renting.
- Providing Adverse Action Notice: If a decision is made against the individual due to their credit report, the entity must provide an adverse action notice explaining the reasons and informing the individual of their rights.
How to Manage and Improve Your Credit History
Managing and improving your credit history is essential for maintaining a positive credit score. Here are some effective tips:
- Check Your Credit Report Regularly: Obtain a copy of your credit report at least once a year to identify errors and discrepancies.
- Pay Bills on Time: Consistent and timely payments are crucial for a healthy credit score. Consider setting up automatic payments to avoid missing due dates.
- Keep Credit Utilization Low: Aim to use less than 30% of your available credit limit. High utilization rates can negatively impact your credit score.
- Avoid Opening Too Many Accounts at Once: Each credit inquiry can lower your score. Only apply for credit when necessary.
- Diversify Your Credit Mix: Having a mix of credit types, such as credit cards, installment loans, and mortgages, can benefit your credit score.
- Address Debts Promptly: If you have outstanding debts, create a plan to pay them off as quickly as possible.
- Consider a Secured Credit Card: If you are building or rebuilding your credit, a secured credit card can help establish a positive payment history.
- Become an Authorized User: If a family member has a good credit history, becoming an authorized user on their credit card can boost your score.
- Limit Hard Inquiries: Be mindful of the number of hard inquiries on your credit report, as too many can harm your score.
- Seek Professional Help if Needed: If you’re struggling with your credit, consider consulting a credit counseling service for personalized guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What does a background credit check show? A background credit check typically reveals an individual’s credit history, outstanding debts, payment history, and any bankruptcies or collections.
- How long does a background credit check take? The duration can vary but generally takes a few minutes to a couple of days, depending on the credit reporting agency.
- Can I check my own credit report? Yes, you can check your own credit report for free once a year from each of the three major credit bureaus.
- Does a background credit check affect my credit score? A soft inquiry does not affect your credit score, while a hard inquiry may lower it temporarily.
- What should I do if I find an error on my credit report? You should dispute the error with the credit bureau and provide any necessary documentation to support your claim.
- How can I improve my credit score? Pay bills on time, keep credit utilization low, and avoid opening too many new accounts at once.
- How often can a lender check my credit? Lenders can check your credit whenever you apply for new credit, but they should obtain your consent.
- Are there laws protecting me from unfair credit checks? Yes, the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) provides consumers with rights regarding credit checks and reporting.
- Can employers conduct credit checks on all job applicants? Employers can conduct credit checks, but they must comply with federal and state regulations and obtain consent.
- What happens if my credit report has a bankruptcy? A bankruptcy can significantly impact your credit score and remain on your report for up to 10 years, but you can rebuild your credit over time.
Conclusion
In summary, background credit checks play a pivotal role in various sectors, influencing lending, hiring, and renting decisions. Understanding the significance of these checks and the factors that affect credit history is vital for individuals and businesses alike. By managing credit effectively and staying informed about credit reports, consumers can ensure a strong financial standing that opens up opportunities for loans, jobs, and housing.
Being proactive about your credit history not only helps you avoid potential pitfalls but also empowers you to achieve your financial goals. With the right knowledge and strategies, anyone can navigate the credit landscape successfully.
 credit.suarajatim.com
credit.suarajatim.com