Credit Score Impact: Affects Financial Life and Tips to Improve It. Your credit score is one of the most critical elements in personal finance. It influences various aspects of your financial life, including loan eligibility, interest rates, and even rental applications. Understanding the credit score impact on your financial stability is essential to navigate effectively in today’s financial world. In this article, we’ll discuss what credit scores are, how they impact your finances, ways to improve them, and provide you with tips and frequently asked questions (FAQs) to help you master your credit health.
What Is a Credit Score?
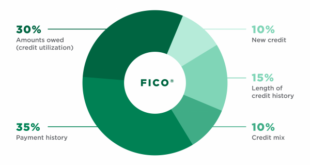
A credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness. It is calculated based on factors such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit, and recent credit inquiries. The higher your score, the better your perceived creditworthiness, which can make it easier to secure loans, mortgages, or credit cards at favorable rates.
How Credit Score Affects Financial Life
1. Loan Approval and Interest Rates
- Credit Score Range and Its Impact: Typically, a higher score (e.g., 700 and above) increases the chances of loan approval and offers lower interest rates, saving you money in the long run.
- High-Interest Rates for Low Scores: A lower score (e.g., below 600) often results in higher interest rates, making loans more expensive over time.
2. Credit Card Approval and Benefits
- Eligibility for Premium Cards: Credit card issuers often reserve the best rewards cards for individuals with higher credit scores, allowing access to benefits such as cashback, travel rewards, and zero-interest promotions.
- Credit Limits and APR: Those with higher scores may be offered higher credit limits and lower annual percentage rates (APRs), making credit cards more affordable and flexible.
3. Mortgage and Real Estate Impacts
- Home Loan Eligibility: A strong credit score is critical when applying for mortgages. A high score can mean a lower interest rate, making your monthly payments more manageable.
- Rental Applications: Many landlords and property managers check credit scores to assess tenant risk. A low score could lead to a rejected rental application or require a higher deposit.
4. Car Loans and Leasing Terms
- Interest Rates on Auto Loans: A good credit score can significantly lower the interest rate on car loans, making car ownership more affordable.
- Lease Terms and Down Payments: Leasing companies often check credit scores and may require higher down payments from applicants with lower scores.
5. Insurance Premiums
- Auto and Home Insurance Costs: Some insurance companies use credit scores as part of their risk assessment models. A lower score can lead to higher premiums, while a high score may qualify you for lower insurance rates.
Factors That Affect Your Credit Score
- Payment History: Making on-time payments is one of the most crucial factors. Late payments or defaults have a negative impact on your score.
- Credit Utilization Ratio: The percentage of available credit you use affects your score. Ideally, keeping it below 30% is recommended.
- Length of Credit History: A longer credit history generally boosts your score, showing lenders your reliability over time.
- Types of Credit: Having a mix of credit types (e.g., credit cards, auto loans) can positively impact your score.
- Recent Inquiries: Each hard inquiry (e.g., for new credit) can slightly lower your score temporarily.
Ways to Improve Your Credit Score
- Pay Bills on Time: Timely payments are essential. Set up automatic payments or reminders to avoid missed payments.
- Keep Balances Low on Credit Cards: Aim for a credit utilization ratio under 30% to keep your score in a favorable range.
- Limit Hard Inquiries: Avoid unnecessary credit applications, as too many inquiries can temporarily reduce your score.
- Build a Longer Credit History: Keep old accounts open to extend your credit history length.
- Diversify Your Credit Portfolio: Having both revolving credit (credit cards) and installment loans (auto loans, mortgages) can boost your score.
- Regularly Check Your Credit Report: Errors in your report can drag down your score. Use a free credit report service to monitor it.
- Consider a Secured Credit Card: If you have a low score or no credit, a secured card can help build credit.
- Negotiate with Creditors: If you’re struggling to pay, contact creditors to explore payment plans rather than missing payments.
- Pay Off Debt: Reducing overall debt can improve your credit utilization ratio, boosting your score.
- Become an Authorized User: Being added as an authorized user on a family member’s card can positively impact your score if they have a good history.
10 Tips to Maintain and Boost Your Credit Score
- Set Payment Alerts: Reminders for bill payments can help you avoid late payments.
- Avoid Maxing Out Credit Cards: Keep usage low even if you have high credit limits.
- Dispute Credit Report Errors: Review your credit report for inaccuracies and dispute them promptly.
- Use Credit Wisely: Avoid overspending; use credit for essential purchases and pay off balances quickly.
- Increase Credit Limits Carefully: A higher limit can improve your utilization rate, but only if you avoid increasing debt.
- Opt for Automatic Payments: Set up automatic payments for consistent, timely payments.
- Minimize New Credit Applications: Multiple inquiries can impact your score. Apply only when necessary.
- Close Accounts Carefully: Closing accounts can reduce your available credit, so consider the effect before closing.
- Educate Yourself: Financial literacy regarding credit is essential for maintaining a strong credit score.
- Seek Professional Advice if Needed: If struggling with debt, consider consulting a credit counselor.
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Credit Score Impact
- What is a good credit score?
- Typically, a score of 700 and above is considered good, while scores above 800 are excellent.
- How often does my credit score update?
- Scores usually update monthly, though it can vary by lender.
- Does checking my credit report affect my score?
- No, checking your credit report is a soft inquiry and doesn’t impact your score.
- Can I remove negative items from my credit report?
- Some negative items, like errors, can be disputed and removed, but legitimate negative items usually stay.
- What’s the difference between a soft and hard inquiry?
- A soft inquiry doesn’t affect your score, while a hard inquiry can lower it temporarily.
- How long do late payments stay on my report?
- Generally, seven years, though the impact diminishes over time.
- Can I improve my score quickly?
- Yes, by paying down debt, making timely payments, and reducing utilization, you may see improvements.
- Do utility payments affect my credit score?
- Generally, they do not unless reported to credit bureaus, though some services now allow utility payments to help build credit.
- Is it better to pay off my credit card in full or leave a balance?
- Paying in full is recommended, as it shows responsible credit use and doesn’t incur interest.
- How does becoming an authorized user help?
- If the primary cardholder has a positive history, it can boost your score through association.
Conclusion
In today’s financial landscape, your credit score significantly influences your financial stability. From securing loans at favorable rates to improving eligibility for premium credit cards and insurance rates, a good credit score opens doors to numerous financial benefits. By understanding the factors that impact your score and implementing responsible credit practices, you can maintain or improve your score, making your financial future brighter.
Staying proactive about your credit score—regularly checking reports, disputing errors, and following the strategies shared in this article—can help you keep your credit healthy. Remember, your credit score is a reflection of your financial responsibility, so prioritize sound financial habits for lasting positive effects on your life.
 credit.suarajatim.com
credit.suarajatim.com