What is a Good Credit Score? An In-Depth Guide to Improving Credit Score. When it comes to personal finance, understanding your credit score is crucial. A good bank score can open doors to financial opportunities, such as lower interest rates, better loan terms, and favorable credit card options. But what exactly is a good bank score, and how can you achieve it?
This article will break down what constitutes a good bank score, factors that affect it, ways to improve your score, and frequently asked questions to help you get on the right track for financial health.
What is a Credit Score?
A bank score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness, based on factors such as your payment history, debt levels, credit history length, types of credit used, and recent inquiries. Credit scores range from 300 to 850, and they help lenders assess the risk of lending to you. Generally, the higher your score, the more likely you are to be approved for loans with favorable terms.
Why is a Good Credit Score Important?
A good bank score can influence many aspects of your financial life. It impacts:
- Loan Approval: Higher scores improve chances for approval.
- Interest Rates: Better credit leads to lower rates.
- Credit Card Options: Higher scores can unlock premium credit card options with perks.
- Employment Opportunities: Some employers check bank scores, especially for finance-related roles.
- Rental Applications: Landlords often require credit checks for rentals.
What is Considered a Good Credit Score?
While each lender may set their own standards, bank score ranges are typically divided as follows:
- Poor (300–579): Considered high risk by lenders.
- Fair (580–669): Higher risk but may still qualify for certain loans.
- Good (670–739): Considered low risk and is often accepted by most lenders.
- Very Good (740–799): Very low risk, typically qualifying for better loan terms.
- Excellent (800–850): Lowest risk, enabling access to the best loan and credit options.
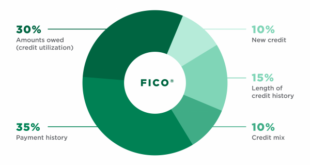
Factors that Affect Your Credit Score
Several key factors influence your bank score, with the most critical ones listed below:
- Payment History (35%): Timely payments are the most significant factor.
- Credit Utilization (30%): Lower credit usage relative to your limit helps improve scores.
- Credit History Length (15%): A longer bank history benefits your score.
- Credit Mix (10%): A variety of credit types, like loans and credit cards, is favorable.
- Recent Credit Inquiries (10%): Numerous bank inquiries in a short period may lower your score.
How to Check Your Credit Score
There are multiple ways to check your bank score:
- Credit Bureaus: Access reports from Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion.
- Bank or Credit Card Statements: Many banks provide freebank scores to customers.
- Credit Monitoring Services: Companies like Credit Karma and Mint offer free credit monitoring.
Steps to Improve Your Credit Score
If you’re looking to improve your bank score, here are some actionable steps:
- Pay Bills on Time: Avoid late payments to maintain a good score.
- Reduce Debt: Lowering your debt can improve your credit utilization rate.
- Limit New Credit Inquiries: Avoid multiple hard inquiries in a short period.
- Maintain Old Accounts: Older accounts contribute to your credit history.
- Use Credit Wisely: Aim for a bank utilization rate of 30% or less.
- Dispute Errors: Review your bank report for errors and dispute them if necessary.
- Use a Secured Credit Card: If rebuilding credit, a secured bank card can be beneficial.
- Avoid Closing Unused Credit Cards: Keeping them open helps your credit utilization ratio.
- Set Up Payment Reminders: Ensure you never miss a payment by setting reminders.
- Seek Professional Help if Needed: Consider bank counseling if your debt is overwhelming.
10 Tips to Maintain a Good Credit Score
- Check Your Credit Score Regularly: Awareness helps in addressing issues early.
- Avoid High Balances on Credit Cards: Lower balances improve credit utilization.
- Set Up Auto Payments: Automate bill payments to avoid late fees.
- Monitor Credit Inquiries: Limit applications for new credit.
- Have a Healthy Credit Mix: Use both credit cards and installment loans.
- Avoid Co-Signing Loans: Responsibility for others’ payments can hurt your score.
- Refrain from Frequent Balance Transfers: Constant transfers may indicate financial instability.
- Focus on Long-Term Financial Health: Build credit slowly and steadily.
- Limit Spending on Credit Cards: Spending within your means helps avoid debt.
- Educate Yourself on Credit: Understanding bank factors leads to better financial decisions.
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is a good credit score? A good bank score is typically between 670 and 739.
- How often should I check my credit score? It’s recommended to check your score at least once every three months.
- Will checking my own credit score hurt my score? No, checking your own score is a “soft inquiry” and does not impact your score.
- Can I improve my credit score quickly? Improving a bank score takes time, but timely payments and reducing debt can help.
- What happens if I miss a payment? Late payments can lower your score and remain on your bank report for seven years.
- What is the difference between a soft and hard inquiry? A soft inquiry does not affect your score, but a hard inquiry can temporarily lower it.
- Does closing a credit card affect my credit score? Yes, it can lower your score by reducing your available credit.
- How long do negative items stay on a credit report? Most stay for seven years, while bankruptcy can last up to ten years.
- Is there a minimum credit score for getting approved for loans? Requirements vary by lender, but a higher score improves approval chances.
- What should I do if I find an error on my credit report? Contact the bank bureau to dispute and correct errors promptly.
Conclusion
Understanding what constitutes a good bank score and how to maintain it is essential for long-term financial health. A score of 670 or higher is generally favorable, providing access to better financial products and terms. By managing your debt, making timely payments, and monitoring your bank report, you can build and maintain a strong bank score. With patience and consistent effort, a good bank score is achievable, opening doors to greater financial opportunities and stability.
 credit.suarajatim.com
credit.suarajatim.com