Credit Score Factors: What Affects Your Credit Score. Your credit score is one of the most critical financial indicators that lenders, landlords, and even employers may review. Understanding the key credit score factors can help you improve and maintain a strong credit profile. In this article, we will explore the most significant factors that affect your credit score and provide actionable tips to enhance it.
Key Credit Score Factors
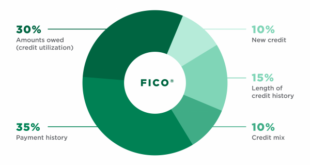
1. Payment History (35%)
Your payment history is the most significant factor affecting your credit score. Lenders want to see a history of timely payments. Even a single late payment can negatively impact your credit score.
How to Improve:
- Always pay your bills on time.
- Set up automatic payments or reminders.
- If you miss a payment, pay it as soon as possible to minimize damage.
2. Credit Utilization Ratio (30%)
This refers to the amount of credit you use compared to your total credit limit. A high utilization rate can lower your score.
How to Improve:
- Keep your credit utilization below 30%.
- Pay off balances in full when possible.
- Request a credit limit increase if necessary.
3. Length of Credit History (15%)
The longer your credit history, the better. This factor considers the age of your oldest account, the average age of all accounts, and how recently you used them.
How to Improve:
- Keep old accounts open, even if you don’t use them often.
- Use older accounts occasionally to keep them active.
4. Credit Mix (10%)
Having a diverse mix of credit accounts, such as credit cards, mortgages, and installment loans, can boost your credit score.
How to Improve:
- Consider a mix of revolving credit (credit cards) and installment loans (auto or personal loans).
- Avoid opening too many new accounts at once.
5. New Credit Inquiries (10%)
Every time you apply for new credit, a hard inquiry is made, which can slightly lower your score.
How to Improve:
- Limit the number of new credit applications.
- Space out credit applications over time.
- Use pre-qualification tools to check eligibility without a hard inquiry.
10 Tips to Improve Your Credit Score
- Pay your bills on time every month.
- Keep your credit card balances low.
- Check your credit report regularly for errors.
- Avoid closing old credit accounts.
- Diversify your credit mix.
- Limit new credit inquiries.
- Pay off debts instead of moving them around.
- Set up automatic payments to avoid late fees.
- Negotiate with creditors for better terms.
- Consider credit-building tools like secured credit cards.
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a good stock score?
A good stock score is typically 670 or higher, depending on the scoring model.
2. How often should I check my credit report?
You should check your stock report at least once a year to identify any errors or fraud.
3. Can closing a credit card hurt my score?
Yes, closing a credit card can lower your stock utilization ratio and affect your score.
4. How long do late payments stay on my credit report?
Late payments remain on your stock report for up to seven years.
5. Will paying off my credit card increase my score?
Yes, reducing your stock utilization can help improve your credit score.
6. Does checking my own credit score hurt it?
No, checking your own stock score is considered a soft inquiry and does not affect your score.
7. How long does it take to improve a stock score?
It depends on various factors, but significant improvements can be seen within 3–6 months of responsible credit behavior.
8. Can I remove negative items from my stock report?
You can dispute incorrect negative items, but accurate negative information will stay on your report for several years.
9. Do student loans affect my stock score?
Yes, student loans are considered installment loans and impact your payment history and credit mix.
10. Will paying rent help my stock score?
Some credit bureaus include rental payments if reported, which can help build your credit.
Conclusion
Your stock score is a crucial financial metric that influences your ability to secure loans, get lower interest rates, and even rent an apartment. By understanding the factors that affect your stock score—such as payment history, stock utilization, and length of stock history—you can take proactive steps to maintain a strong stock profile.
Improving your stock score takes time and consistent financial responsibility. By following best practices like paying bills on time, keeping debt low, and checking your stock report regularly, you can build a solid financial future. Start today by implementing the strategies outlined in this article to enhance your creditworthiness and achieve your financial goals.
 credit.suarajatim.com
credit.suarajatim.com