Credit Score Information: Everything You Need to Know. A credit score is a numerical representation of a person’s creditworthiness, typically ranging from 300 to 850. Lenders, banks, and financial institutions use this score to assess the risk of lending money to individuals. The higher the score, the more trustworthy a borrower appears to be.
How is a Credit Score Calculated?
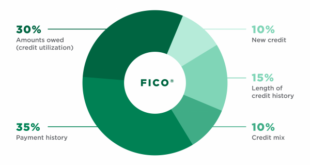
Credit scores are calculated based on five primary factors:
- Payment History (35%) – Timely payments on credit accounts significantly impact your score.
- Credit Utilization (30%) – The ratio of credit used versus the total available credit.
- Length of Credit History (15%) – The longer your credit history, the better your score.
- Credit Mix (10%) – Having different types of credit accounts, such as credit cards, auto loans, and mortgages, can improve your score.
- New Credit Inquiries (10%) – Too many recent hard inquiries can lower your score.
Why is a Credit Score Important?
A credit score affects various aspects of financial life, including:
- Loan Approval – Banks and lenders use credit scores to determine eligibility for loans.
- Interest Rates – Higher scores often mean lower interest rates.
- Rental Applications – Landlords may check your credit score before renting an apartment.
- Employment Opportunities – Some employers review credit reports as part of background checks.
How to Check Your Credit Score
You can check your credit score through:
- Credit Bureaus – Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion offer credit reports.
- Credit Card Issuers – Many banks provide free credit score access.
- Online Credit Monitoring Services – Websites like Credit Karma or MyFICO.
Factors That Can Lower Your Credit Score
Several factors can negatively impact your credit score, including:
- Late or missed payments
- High credit card balances
- Applying for too many new credit accounts
- Defaulting on loans
- Closing old accounts, which shortens credit history
How to Improve Your Credit Score
Improving your credit score requires consistent effort. Here are some steps to follow:
- Pay bills on time – Avoid late payments to maintain a good score.
- Reduce credit utilization – Keep your credit usage below 30%.
- Avoid opening too many accounts – Each new account application can lower your score.
- Dispute errors on your credit report – Mistakes can impact your score unfairly.
- Keep old accounts open – Older accounts help build a strong credit history.
How Long Does It Take to Improve a Credit Score?
Improving a credit score depends on the factors affecting it. Some changes, like paying off debts, may show results in a few months, while serious issues like bankruptcy can take years to recover from.
The Impact of Credit Score on Loans and Mortgages
Your credit score directly affects loan approvals and interest rates. Here’s how:
- Excellent (750-850) – Best interest rates and easy approval.
- Good (700-749) – Competitive rates with minor restrictions.
- Fair (650-699) – Higher interest rates, but still eligible for loans.
- Poor (600-649) – Limited options, high rates, or secured loans required.
- Very Poor (300-599) – High rejection rates; requires significant credit rebuilding.
10 Tips to Maintain a Healthy Credit Score
- Pay your bills on time every month.
- Keep your credit utilization below 30%.
- Regularly check your credit report for errors.
- Avoid opening multiple new credit accounts at once.
- Keep old credit accounts open to maintain credit history.
- Limit hard inquiries on your credit report.
- Diversify your credit mix with different account types.
- Pay off debts rather than moving them around.
- Set up automatic payments to avoid late fees.
- Use credit responsibly and plan major purchases.
10 Frequently Asked Questions About Credit Scores
1. What is the best credit score?
The highest credit score is 850, but anything above 750 is considered excellent.
2. How often should I check my credit score?
You should check your credit score at least once a year or more frequently if you’re applying for a loan.
3. Do checking my credit score lower it?
No, checking your own credit score is considered a soft inquiry and does not affect your score.
4. Can I improve my credit score quickly?
Yes, by paying off debts, making timely payments, and lowering credit utilization.
5. Do unpaid utility bills affect my credit score?
Yes, if they are reported to collections, they can negatively impact your score.
6. Can I remove negative items from my credit report?
If there are errors, you can dispute them with the credit bureau to have them removed.
7. How long do negative items stay on my credit report?
Most negative items stay on your credit report for seven years, except for bankruptcies, which can last up to 10 years.
8. What is a good credit utilization ratio?
A credit utilization ratio below 30% is considered good.
9. Will closing a credit card improve my score?
Not necessarily. Closing a card can reduce your credit history length and increase utilization, both of which can lower your score.
10. Can student loans affect my credit score?
Yes, timely payments help improve your score, while missed payments can hurt it.
Conclusion
Understanding credit score information is crucial for financial success. Your credit score impacts your ability to secure loans, get favorable interest rates, and even rent an apartment. Maintaining a good credit score requires discipline, timely payments, and responsible credit usage.
By following best practices such as keeping your utilization low, checking your report regularly, and making on-time payments, you can improve or maintain a strong credit score. Managing credit wisely ensures long-term financial health and opens doors to better financial opportunities.
 credit.suarajatim.com
credit.suarajatim.com